Notice
250x250
Recent Posts
Recent Comments
Link
넘치게 채우기
LIS(Longest Increasing Subsequence) - O(nlogn)으로 진짜 LIS를 구하기 본문
컴퓨터과학/알고리즘
LIS(Longest Increasing Subsequence) - O(nlogn)으로 진짜 LIS를 구하기
riveroverflow 2024. 10. 21. 12:32728x90
반응형
O(nlogn)으로 LIS의 길이를 구하는 가장 간단한 코드는 다음과 같다:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
arr = {10, 9, 2, 5, 3, 7, 101, 18};
vector<int> lis;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
auto it = lower_bound(lis.begin(), lis.end(), arr[i]);
if (it == lis.end()) {
lis.push_back(arr[i]);
} else {
*it = arr[i];
}
}
cout << lis.size() << "\n";
return 0;
}그러나 이는 길이만 구할 뿐, 순서가 뒤섞여서 실제 LIS는 아니다.
아래 코드는 실제 LIS를 구하는 가장 빠른 코드이다.
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
vector<int> findLIS(const vector<int> &nums) {
if (nums.empty())
return {};
int n = nums.size();
vector<int> tails;
vector<int> tails_indices;
vector<int> parents(n, -1);
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
int pos = lower_bound(tails.begin(), tails.end(), nums[i]) - tails.begin();
if (pos == tails.size()) {
tails.push_back(nums[i]);
tails_indices.push_back(i);
} else {
tails[pos] = nums[i];
tails_indices[pos] = i;
}
if (pos != 0) {
parents[i] = tails_indices[pos - 1];
}
}
int lis_length = tails.size();
vector<int> lis(lis_length);
int k = tails_indices.back();
for (int i = lis_length - 1; i >= 0; --i) {
lis[i] = nums[k];
k = parents[k];
}
return lis;
}
int main() {
vector<int> nums = {10, 9, 2, 5, 3, 7, 101, 18};
vector<int> lis = findLIS(nums);
cout << "Longest Increasing Subsequence: ";
for (int num : lis) {
cout << num << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
tails: 현재까지 발견된 Increasing subsequence의 끝 값을 저장한다.
tails_indices: tails에 저장된 값들의 인덱스를 저장한다.
parents: 각 원소가 이전 원소와 연결되는 인덱스를 저장하여, LIS복원에 쓰인다.
순차적으로 nums를 순회하면서, 다음을 한다:
우선, 이진 탐색(lower_bound)로 위치 pos를 찾는다.
만약 pos가 맨 뒤라면, 새로운 길이의 LIS를 찾은 것이다. tails와 tails_indices에 추가한다.
tails[pos]를 nums[i]로 업데이트하여 더 작은 값을 유지한다.
parents배열을 업데이트하여 나중에 LIS를 복원할 수 있게 된다.
tails_indices의 마지막 인덱스부터 해서, parents배열을 따라가며, 실제 LIS를 만든다.
이는 역순으로 채워야 한다.(부모가 이전 요소니까)
출력값은 다음과 같다:
❯ g++ -std=c++17 -o LIS.out LIS.cpp && ./LIS.out
Longest Increasing Subsequence: 2 3 7 18
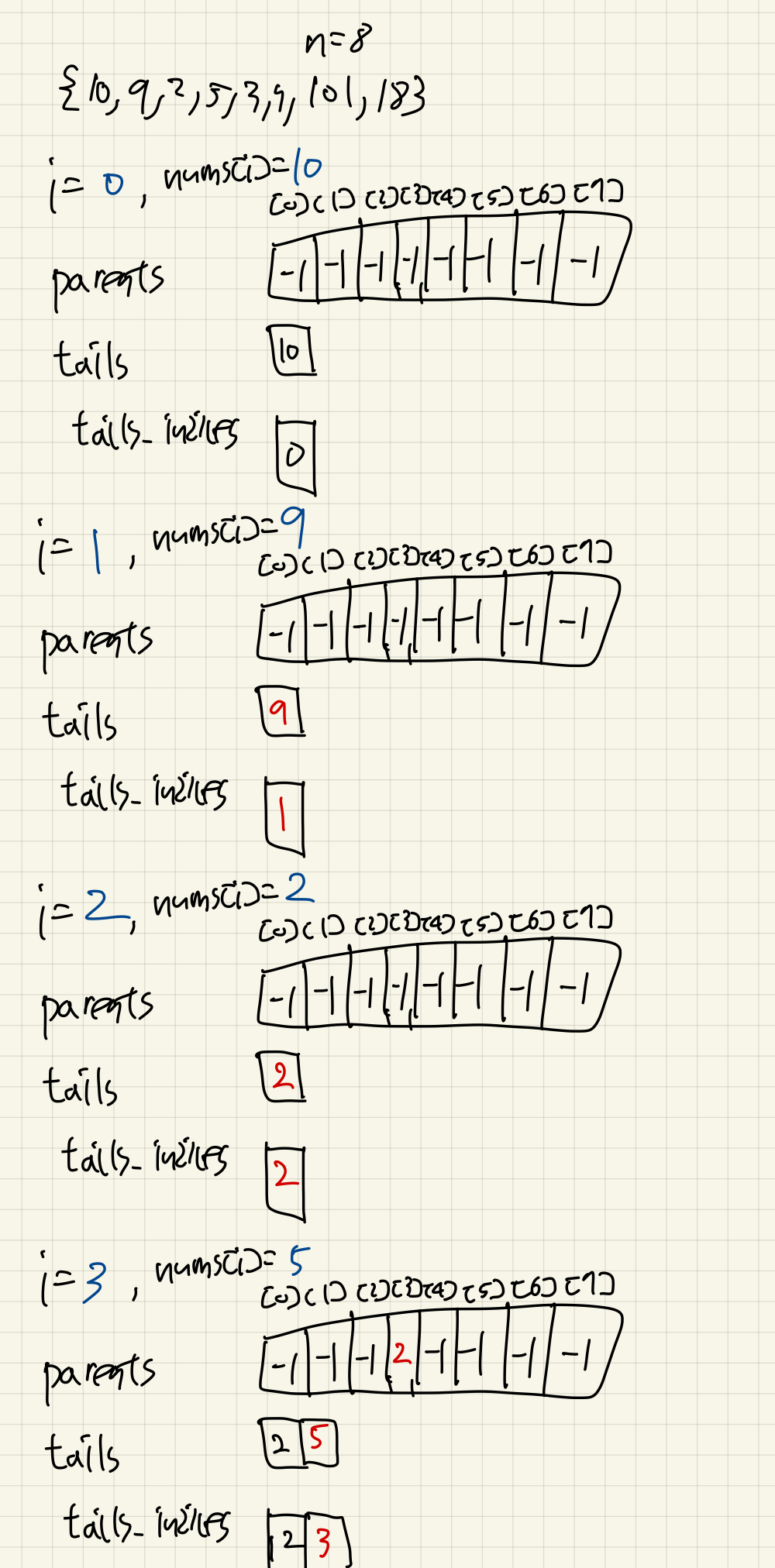
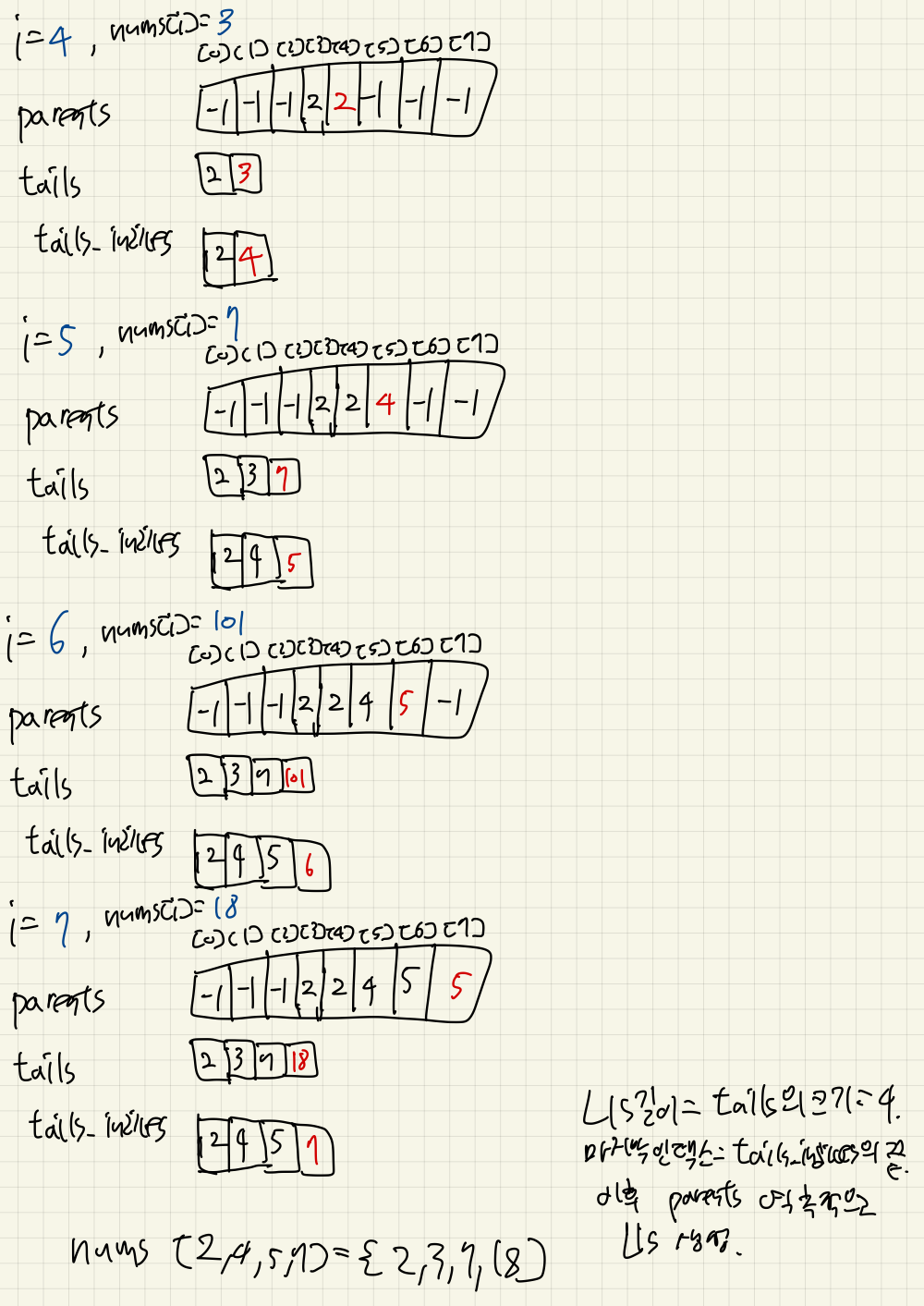
아래는 Dry-Run이다:
언뜻 보면, tails가 LIS같아보일 수는 있는데, 더 복잡한 케이스에서는 그렇지 않다.
정확한 LIS를 만들기 위해서는, parents를 추적해야 한다.
728x90
반응형
'컴퓨터과학 > 알고리즘' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 세그먼트 트리와 지연전파 (Segment Tree, with lazy propagation) (0) | 2025.02.20 |
|---|---|
| MITM(Meet-in-the-Middle): n <= 40에 대한 Subset Sum 문제를 위한 방법 (0) | 2024.12.06 |
| 오일러 경로와 오일러 회로(Eulerian Trail, Eulerian Circuit) (0) | 2024.10.16 |
| 문자열 패턴 검색: 3 - KMP 알고리즘 (0) | 2024.09.20 |
| 문자열 패턴 검색: 2 - 라빈-카프 알고리즘 (Rabin-Karp Algorithm) (0) | 2024.09.20 |

